
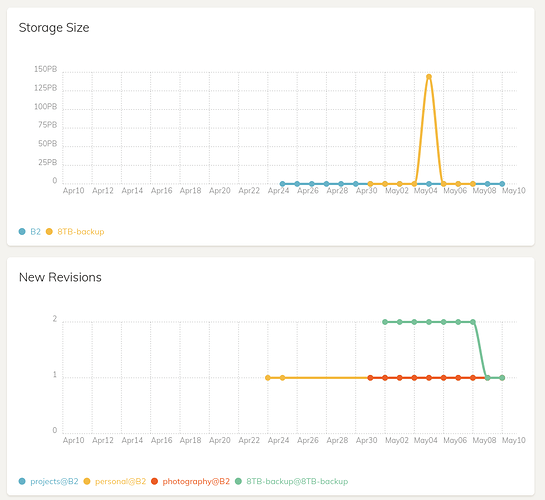
There have been lengthy discussions on this topic such as here and here. At the same time, if the directory where the file original resides is backed up again (using the -hash option), then the hole left by this file will also cause several new chunks to be generated. As a result, when a file larger than the average chunk size is moved or renamed, the pack-and-split procedure will produce several new chunks at the beginning and the end of the file. On the other hand, when a directory consisting of many small files is to be moved or renamed, because these small files will be packed in the same order, most of chunks generated after the move or rename will remain unchanged, except for a few at the beginning and at the end that are likely affected by files in adjacent directories.Īnother implication is that chunks do not usually align with file boundaries. For instance, any change on a file that is 100K bytes or so will cause the entire file to be uploaded again (as a separate chunk, or part of a chunk if there are other changed files). First, any files smaller than the minimum chunk size will not individually benefit from deduplication.
This pack-and-split method has two implications. The default settings of the init command would generate chunks that are 4M bytes on average (although the actual averages may vary), at least 1M bytes and at most 16M bytes. This imaginary tar file is then split into chunks, using a variable size chunking algorithm. Of course, this is only conceptual, otherwise Duplicacy would have quickly run out of memory in most use cases. First, all files to be backed up are packed together, in an alphabetical order, as if it were building an imaginary tar file. Duplicacy adopts a unique pack-and-split method to split files into chunks.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
